Welcome to Matrix Education
To ensure we are showing you the most relevant content, please select your location below.
Select a year to see courses
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Get HSC exam ready in just a week
Select a year to see available courses
Science guides to help you get ahead
Science guides to help you get ahead
Are you ready for your Year 11 Biology Yearly Exam? Assess your exam-readiness with these commonly asked exam questions.

Join 75,893 students who already have a head start.
"*" indicates required fields
You might also like
Related courses
The Matrix Year 11 Biology Yearly Exam Paper contains questions based on the new Year 11 Biology syllabus. This practice paper covers the four modules of the Year 11 Biology course:
We have listed below some of the most popular exam questions for your quick reference. You can download the free Matrix Year 11 Biology Practice Paper:
Test your knowledge and refine your exam skills with this complete HSC practice paper Fill out your details below to get this resource emailed to you. "*" indicates required fields
Get your FREE Year 11 Biology Practice Paper

Get your FREE Year 11 Biology Practice Paper
Commonly asked exam questions on Module 1 Cells as the Basis of Life are:
Which of the following organelles in a eukaryote cell are correctly matched with their function?
| Structure | Function | |
| (A) | Rough endoplasmic reticulum | Protein synthesis |
| (B) | Smooth endoplasmic reticulum | ATP synthesis |
| (C) | Mitochondria | Nucleotide degradation |
| (D) | Lysosomes | Lipid synthesis |
Refer to the following diagram.
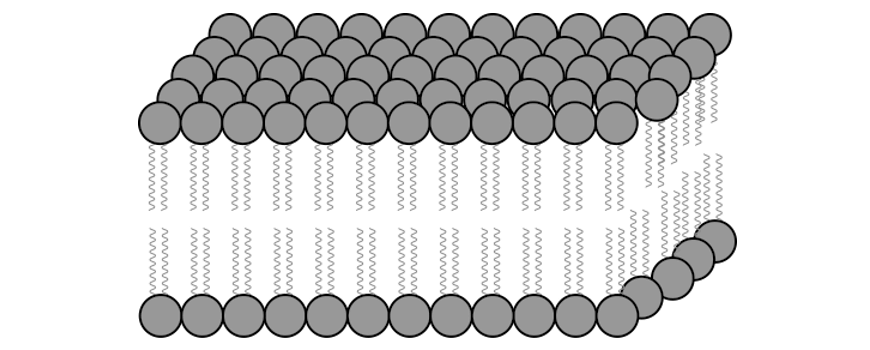
What does the diagram depict?
Liver contains an enzyme called catalase. This enzyme acts on the substrate hydrogen peroxide to produce water and oxygen gas.
Given the information above, design a first-hand investigation to determine the effect of temperature on enzyme activity.
Be one step ahead of your peers with advanced completion of contents before it’s taught at school. You’ll gain an in-depth knowledge and understanding of the key concepts for exam success.
Don't just memorise. Understand.
Expert teachers, weekly quizzes, one-to-one help! Ace your next Biology assessment with Matrix+ Online.
Commonly asked exam questions on Module 1 Organisation of Living Things are:
A veterinarian was presented with a badly damaged roadkill and asked to identify whether it was a carnivorous tiger quoll or an herbivorous ringtail possum.
How might the vet identify the animal through dissection?
(A) A ringtail possum will have a short simple digestive system compared to the quoll.
(B) A ringtail possum will have a stomach, but a tiger quoll will not.
(C) A ringtail possum will have a caecum, but a tiger quoll will not.
(D) A ringtail possum will have an appendix, but a tiger quoll will not.
Identify the correct summary of gas exchange in these four animals:
| Earthworms | Insects | Fish | Amphibian | |
| (A) | Buccal pumping and diffusion across skin | Spiracles and tracheae | Counter current exchange | Diffusion across skin |
| (B) | Diffusion across skin | Counter current exchange | Spiracles and tracheae | Buccal pumping and diffusion across skin |
| (C) | Diffusion across skin | Spiracles and tracheae | Counter current exchange | Buccal pumping and diffusion across skin |
| (D) | Spiracles and tracheae | Diffusion across skin | Counter current exchange | Buccal pumping and diffusion across skin |
Outline the current theory for the movement of materials in xylem tissue.
Commonly asked exam questions on Module 3 Biological Diversity are:
Koalas have a low metabolic rate that allows them to digest food for long enough to extract energy from their high fibre diet. As a result, koalas may sleep for more than 20 hours per day.
How should this ability be described?
(A) A structural adaptation
(B) A physiological adaptation
(C) A behavioural adaptation
(D) Convergent evolution
New Zealand does not have any native mammals. However, a small flightless ratite bird, the Kiwi, has a similar appearance and habitat to small insectivorous mammals. It has plain brown feathers, lives in a burrow and has long thin feathers near its beak which act like whiskers.
Explain how a bird and a mammal could end up with similar characteristics.
The rate of infections by antibiotic-resistant bacteria has been increasing since antibiotics were first introduced.
(A) Identify TWO ways that an individual bacterium can obtain resistance to antibiotics. (2 marks)
(B) Explain how natural selection can produce a population of bacteria that is resistant to antibiotics. (3 marks)
Commonly asked exam questions on Module 4 Ecosystem Dynamics are:
The Tasmanian tiger or thylacine represents an example of an extinction of an Australian mammal species.
What is the most likely cause of the extinction of the thylacine?
(A) The activity of early Australians in managing areas of land with fire.
(B) Hunting since European settlement.
(C) The natural decline in global biodiversity.
(D) The change from cool and wet conditions to hot and arid on mainland Australia.
Native palm trees and other rainforest type plants are found around a number of waterholes in the dry centre of Australia.
Which one of the following explanation for this would best fit our knowledge of Australia’s ecosystems?
(a) The plants must have been transported unwittingly by animals travelling from waterhole to waterhole, probably by seeds in their dung.
(b) They evolved from local desert plants.
(c) They are remnants of a more widespread rainforest vegetation which once covered the whole area.
(d) They are early evidence of climate change – global warming is increasing rainfall in the centre of Australia.
The following diagram illustrates the relative positions of Australia and Antarctica during the Cretaceous period.
Which of the following statements about Australia’s past is correct?
(A) As Australia drifted north, glaciers began to form in Australia’s interior.
(B) As Australia drifted north, its overall climate became hotter and more arid.
(C) As Australia drifted north, individuals began to adapt to the change in climate.
(D) All of the above
Written by Matrix Science Team
The Matrix Science Team are teachers and tutors with a passion for Science and a dedication to seeing Matrix Students achieving their academic goals.© Matrix Education and www.matrix.edu.au, 2023. Unauthorised use and/or duplication of this material without express and written permission from this site’s author and/or owner is strictly prohibited. Excerpts and links may be used, provided that full and clear credit is given to Matrix Education and www.matrix.edu.au with appropriate and specific direction to the original content.