Welcome to Matrix Education
To ensure we are showing you the most relevant content, please select your location below.
Select a year to see courses
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Get HSC exam ready in just a week
Select a year to see available courses
Science guides to help you get ahead
Science guides to help you get ahead

In the Beginner’s Guide to ATAR and Scaling (VCE), we explained how your study score is your rank reflecting how well you performed in a subject compared to other students across Victoria. This score helps determine your ATAR (Australian Tertiary Admission Rank), which universities use for admission.
An in-depth explanation of VCE and scaling with strategies from top-performing students. Fill out your details below to get this resource emailed to you. "*" indicates required fields
Free 2025 VCE ATAR & Scaling Guide Download

Free 2025 VCE ATAR & Scaling Guide Download
Now, let’s break down the process, step-by-step, to help you understand how your study score is calculated.
Your study score comes from three areas in each study:
Example:
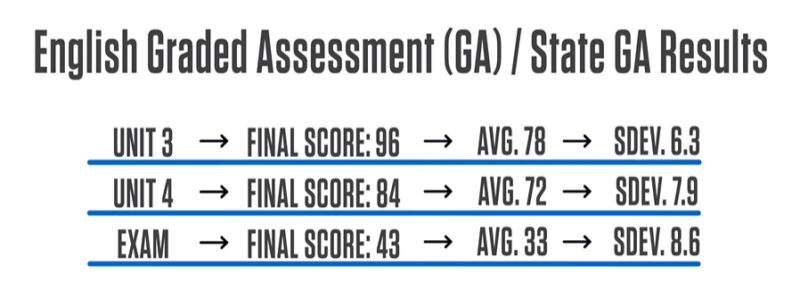
Your raw scores from these assessments are adjusted to account for differences in difficulty and performance. This adjusted score is called a standardised score.

To calculate the final VCE study score, the VCAA (Victorian Curriculum And Assessment Authority) combines the standardised scores for each of your Graded Assessments (GA). Keep in mind that each type of assessment has a different weight in the final score:
This means each part of your assessments contributes a certain percentage to your overall study score.
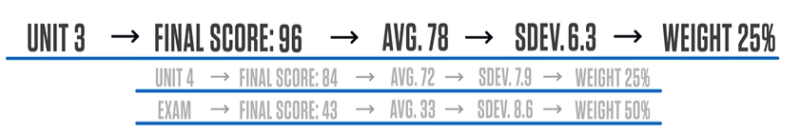
The weighted scores are combined to get your summative weighted standardised GA score:
(Standardised Unit 3 Score×0.25)+(Standardised Unit 4 Score×0.25)+(Standardised Exam Score×0.50) = your summative weighted standardised GA score
After calculating everyone’s summative weighted standardised GA scores, students are ranked from highest to lowest based on their total scores.
Then, these ranks are adjusted to fit a normal distribution (a bell curve). This means scores are spread out with an average of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.
Finally, these adjusted scores are converted to a scale where the average score is 30 and the standard deviation is 7. This means most study scores will be between 23 and 37. The final rank you receive after this process is your actual study score.
Let’s say Mary’s scores were:
Here’s how to calculate Mary’s final study score:
(Standardised Unit 3 Score×0.25)+(Standardised Unit 4 Score×0.25)+(Standardised Exam Score×0.50) = your final weighted standardised GA score
(1.67×0.25)+(2.00×0.25)+(2.50×0.50)
This works out to:
0.4175+0.50+1.25=2.16750
So Mary’s final weighted standardised GA score is around 2.17.
If Mary’s normalised score falls at 1.67 on the adjusted scale, it would translate to a study score slightly above 40, depending on how other students performed that year.
Scaling adjusts your study score based on the difficulty of the subject. This helps make sure your score is fair compared to other subjects. Read more about scaling your study score in Part 2.
Yes, how well you do in school can influence your study score. Here’s how:
Your overall performance in school, like how well you study, participate, and complete assignments, can affect your study score. Good habits and strong performance throughout the year typically lead to a higher study score.
By following these tips and understanding how your study score is calculated, you’ll be better prepared to manage your studies and aim for a great ATAR. Good luck!
Now, let’s look at scaling your VCE study score.
© Matrix Education and www.matrix.edu.au, 2023. Unauthorised use and/or duplication of this material without express and written permission from this site’s author and/or owner is strictly prohibited. Excerpts and links may be used, provided that full and clear credit is given to Matrix Education and www.matrix.edu.au with appropriate and specific direction to the original content.